In recent years, the European Commission has taken significant steps to enhance data privacy and security by issuing various directives to establish secure channels for individuals to submit evidence while preserving their anonymity (known as whistleblowing channels). These directives emphasize the importance of protecting user identities while preventing intentional misuse of sensitive information. One of the directives that has gained more relevance is the EU Directive 2019/1937.
The EU 2019/1937, the Wishtleblowing directive, which came into effect on December 16, 2019, focuses on organizations maintaining secure whistleblowing channels. Those channels are aimed to support complaints relating to
- Public procurement
- Financial services, products and markets; prevention of money laundering and terrorist financing money laundering and terrorist financing
- Product safety and conformity safety of road transport, inland waterways and in the rail and maritime sectors; and rail and maritime sectors
- Environmental protection, from waste management to chemical products chemicals radiation protection and nuclear safety
For achieving this, several means of complaint must be developped
- Internal channels: all private companies with fifty or more employees and all public entities should establish effective whistleblower effective whistleblowing channels that ensure confidentiality; public bodies with fewer than fifty employees and public bodies with less than 50 employees and municipalities with less than 10,000 may be exempted.
- External channels: the relevant national authorities should establish channels for confidential reporting.
- Monitoring procedures and deadlines for handling complaints received by internal and external channels.
In alignment with the principles of its research lines, the GICP group has crafted several Proofs of Concept for privacy-respectful protocols designed to facilitate anonymous reporting and whistleblowing. These protocols are a result of extensive research and innovation and combine crucial elements like authorization, access control, and immutability to establish a high level of trust among honest users. At the same time, they feature mechanisms that can efficiently uncover and mitigate the actions of malicious users.
To achieve such extensive privacy goals, the protocols rely upon cryptographic primitives such as ephemeral key exchanges and encryption, group signatures, and distributed ledger technologies. Ephemeral key exchanges provide secure communication channels, ensuring that messages and evidence remain confidential while ensuring unlinkability to public keys. Encryption further enhances data protection, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized parties to intercept or decipher the transmitted information. The available options provide for procedural whistleblower identity protection: the recipient of the report is trusted
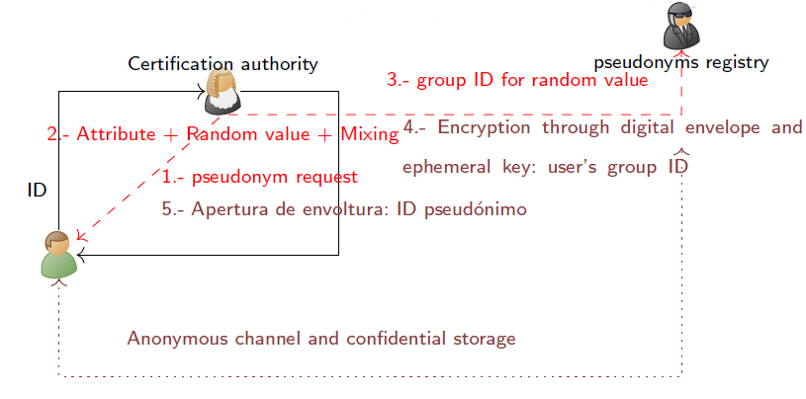
Group signatures are pivotal in the context of privacy-respectful protocols. They enable users to sign documents or submit evidence without revealing their real identity and hiding it within the context of a group. This key feature is instrumental in preserving the anonymity of those providing information. At the same time, the mechanisms inside these protocols enable the uncovering of malicious users under a certain agreement between parties. In addition, robust remote user registration procedures with privacy protection are used, mainly remote attestation and 2FA using ARM/RISC-V based TEE and pseudonymous identities.
Finally, distributed ledgers, such as blockchain, play a vital role in ensuring the immutability of the collected evidence. By storing information in a decentralized and tamper-proof manner, these technologies establish trust in the integrity of the data. Furthermore, our integration has been deployed both with Hyperledger Fabric and Besu, providing two models for the user of the protocols.
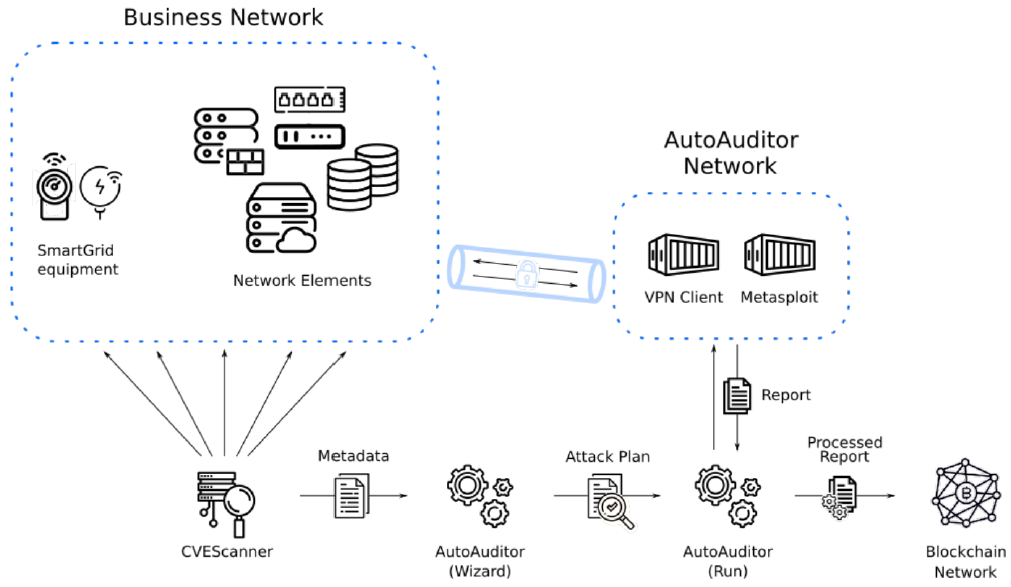
The combination produces a privacy-compliant infrastructure that users can rely upon for various use cases such as e-commerce, electronic vote, industry 4.0 and 5G and 6G network attestation.